ACE-031: Exploring the Frontier of Muscle Growth Research
Greetings, fellow science enthusiasts! Today, we're delving into the intriguing world of ACE-031, known as Ramatercept. With over a decade of peptide research, I'm thrilled to share my insights on this fascinating molecule. Remember, our exploration is purely from a scientific and educational perspective, focusing on its potential in research settings.
What is ACE-031?
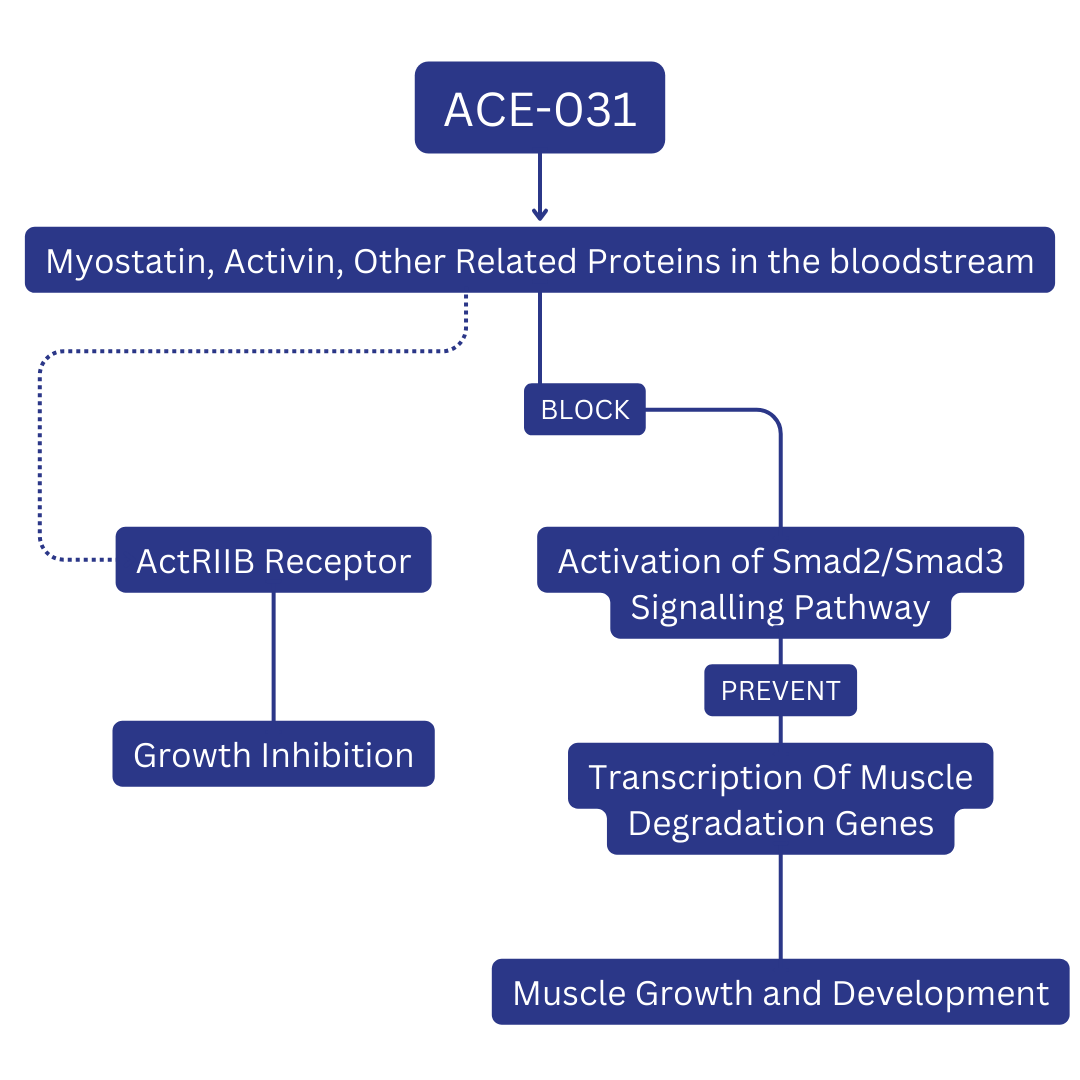
ACE-031 is a fusion protein comprising activin receptor type IIB and IgG1-Fc parts. It's a soluble form of the type IIB activin receptor (ACVR2B), a key player in regulating muscle growth. The primary aim of ACE-031 is to counteract the inhibitory effect on muscle development, offering a ray of hope in potential therapies for myopathies like Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
However, it's crucial to note that ACE-031's clinical development encountered hurdles. Safety concerns, including severe adverse effects like nosebleeds and gum bleeding, led to the premature termination of its clinical trials. Thus, while its research potential remains significant, its application in humans is still under scrutiny.
Mechanism of Action
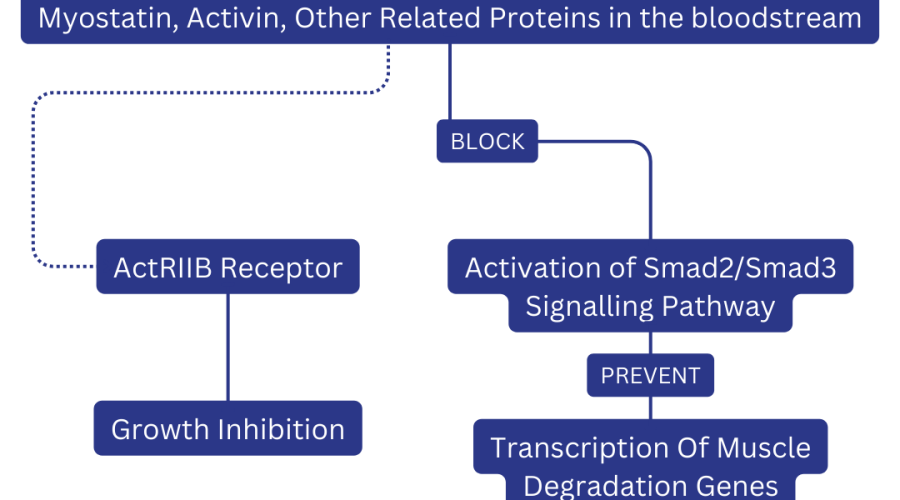
ACE-031 operates by binding to myostatin and other negative regulators of muscle mass. Myostatin, a protein that naturally limits muscle growth, is effectively neutralised by ACE-031. This suppression leads to increased muscle mass, making ACE-031 a subject of interest for addressing muscle-wasting diseases such as DMD. Moreover, it impacts bone metabolism, fat storage, and sperm health.
ACE-031 vs Other Myostatin Inhibitors
The uniqueness of ACE-031 lies in its specific action mechanism. It targets myostatin and related proteins by binding to them, a distinct approach compared to other myostatin inhibitors. This selectivity stems from its fusion protein structure, combining activin receptor type IIB with IgG1-Fc. This structure enables ACE-031 to interfere with ActRIIB receptors, which is crucial in the regulatory effects of myostatin and other molecules like activins. By disrupting these pathways, ACE-031 fosters muscle cell growth and differentiation.
Nevertheless, despite its promising mechanism, ACE-031's journey in clinical applications was halted due to safety concerns, a crucial point to remember in the context of its research and potential use.